3D printing and its importance in dentistry
3D printing and its importance in dentistry
3D Printing in Dentistry
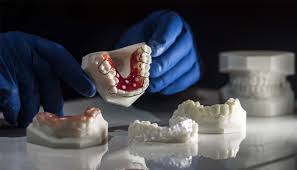
3D printing and its importance in dentistry
Introduction to 3D Printing in Dentistry
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is a technology that significantly transforms various industries, notably dentistry. This innovative process involves creating three-dimensional objects by depositing materials layer by layer, guided by digital models. In dentistry, this technology has catalyzed a range of applications, from producing dental implants and crowns to creating orthodontic devices and surgical guides. The precise nature of 3D printing allows for the creation of highly customized dental solutions, tailored to individual patient needs.
The operation of 3D printing begins with a digital 3D design, which can be generated using computer-aided design (CAD) software or by scanning an existing object with 3D imaging technology. Once the design is finalized, the 3D printer interprets this digital model and begins to manufacture the object through various techniques such as stereolithography (SLA), selective laser sintering (SLS), or fused deposition modeling (FDM). These methods utilize different materials, including biocompatible resins and metal powders, to produce durable and aesthetically pleasing dental products.
The emergence of 3D printing in dentistry began gaining traction in the early 2010s as technology advanced and the costs of printers decreased. Since then, the adoption of 3D printing by dental practitioners has surged, driven by the demand for efficiency, cost reduction, and enhanced patient outcomes. The ability to create accurate prototypes and final products rapidly, on-site, reduces the wait time for patients, making dental procedures more accessible. Additionally, 3D printing promotes sustainable practices in dentistry by minimizing material waste, thereby aligning with eco-friendly initiatives.
As the technology continues to evolve, the potential applications of 3D printing in dentistry are expanding, leading to innovations that could redefine dental care practices. In the sections that follow, we will explore the various benefits and specific applications of this revolutionary technology in the dental industry.
Benefits of 3D Printing for Dental Professionals
The advent of 3D printing technology in dentistry has ushered in a new era of possibilities for dental professionals. One of the most significant advantages is the enhancement of precision and customization in dental procedures. Traditional methods often involved time-consuming and imprecise processes, leading to suboptimal outcomes. In contrast, 3D printing allows for the creation of highly accurate dental models and prosthetics that fit individual patient anatomies. This level of customization not only improves the quality of care but also increases patient satisfaction.
Another noteworthy benefit of 3D printing is the reduction in production times for dental appliances. Conventional manufacturing techniques can take several weeks to deliver products such as crowns, bridges, or orthodontic aligners. However, with 3D printing, dental professionals can produce these items on-site, significantly decreasing the waiting time for patients. This efficiency not only enhances the patient experience but also allows for more rapid treatment planning.
Cost-effectiveness is yet another compelling reason for dental practices to adopt 3D printing technology. While the initial investment in 3D printers may seem substantial, the long-term savings are considerable. By streamlining workflows and minimizing reliance on external laboratories, dental practices can significantly reduce labor and material costs. In addition to operational savings, 3D printing can lead to greater profitability as practices are better equipped to handle increased patient loads with faster turnaround times.
Overall, the incorporation of 3D printing into dentistry presents various benefits for dental professionals. From enhanced precision and reduced production times to improved cost-effectiveness, this technology not only transforms workflows but also significantly uplifts the patient experience. As dental practices continue to embrace these advancements, the potential for growth and success becomes increasingly evident.
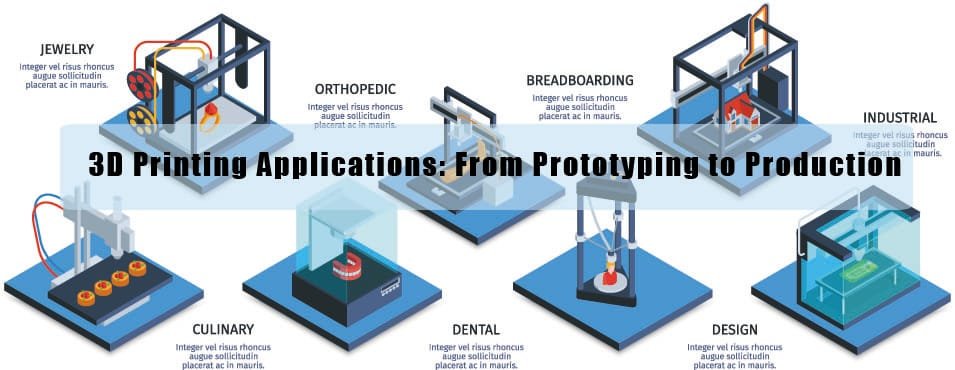
Applications of 3D Printing in Dentistry
3D printing and its importance in dentistry
The advent of 3D printing technology has heralded a new era within the field of dentistry, providing innovative solutions that augment the capabilities of dental professionals. One of the primary applications is the creation of dental models. Traditionally, crafting these models involved labor-intensive processes, but 3D printing has revolutionized this by producing accurate replicas of patients’ oral cavities in a fraction of the time. This enables dentists to plan treatments more effectively while increasing the precision of dental procedures.
Additionally, 3D printing is instrumental in developing surgical guides. These guides assist surgeons during complex procedures, ensuring that implants are placed with optimal accuracy. For instance, a study highlighted a dental practice that utilized 3D-printed surgical guides to facilitate successful implant placement for challenging cases, significantly improving patient outcomes. The adaptability of 3D printing ensures that these guides are customized to fit individual patients, thus enhancing the precision of surgical interventions.
The realm of orthodontics has similarly benefited from this technology. Orthodontic appliances, including braces and aligners, can now be swiftly manufactured using 3D printers. This allows for personalized treatment options that cater specifically to the unique dental structure of each patient. Several case studies have demonstrated how orthodontic practices have reduced lead times by as much as 75% by employing 3D printing, resulting in increased patient satisfaction.
Moreover, the production of crowns and dentures through 3D printing further illustrates its transformative impact in dentistry. By simulating the final product accurately, 3D-printed crowns can be produced with higher fidelity, allowing for a seamless fit. The use of this technology streamlines the production process, significantly reducing the time patients need to wait for prosthetic solutions. Collectively, these applications underscore the versatility and effectiveness of 3D printing technology in enhancing dental practices and improving overall patient care.
Future Trends and Challenges in 3D Printing for Dentistry
The future of 3D printing in dentistry holds significant promise, with ongoing advancements continually reshaping how dental care is delivered. Emerging trends, such as the development of bio-printing technologies, are expected to enhance regenerative dental procedures. This innovative approach enables the creation of living tissue constructs, potentially revolutionizing treatments for periodontal disease and tooth regeneration. Coupled with advancements in materials, such as biocompatible resins and metal alloys, dental professionals can expect increased accuracy and longevity in dental prosthetics and restorations.
Another key trend is the integration of artificial intelligence with 3D printing processes. AI algorithms can optimize design and production workflows, significantly reducing production times and allowing for more complex geometries that traditional techniques cannot achieve. As digital workflows become standard in dental practices, the integration of 3D scanning and computer-aided design (CAD) will facilitate a seamless transition from initial consultations to final product delivery.
However, despite these advancements, several challenges remain. One significant issue is the regulatory environment governing 3D printing in dentistry. As the technology rapidly evolves, regulatory agencies are striving to keep pace, creating uncertainty around compliance and approval processes. Dental professionals must stay informed about changes in regulations to ensure that their practices remain compliant while delivering optimal patient care.
Additionally, the learning curve associated with adopting 3D printing technology can be steep for some dental professionals. Transitioning from traditional techniques to digital methodologies necessitates not only technical training but also a shift in mindset. Continuous education and training will be vital to successfully integrating this transformative technology into dental practices.
In conclusion, the future of 3D printing in dentistry is bright, marked by exciting trends and innovations. While challenges exist, the potential benefits warrant continued exploration and adaptation within the field, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes and expanded treatment possibilities.