Ultimate 3D Printing

The Ultimate Guide to 3D Printing: Transforming Ideas into Reality
Understanding 3D Printing Technology
Ultimate 3D Printer Q&A 2024!
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a transformative technology that creates three-dimensional objects from a digital file. This process involves layering materials, allowing for intricate designs and structures that traditional manufacturing methods may struggle to achieve. The fundamental principle of 3D printing revolves around converting a virtual model into a physical object by adding material layer by layer. This contrasts sharply with subtractive manufacturing, where material is cut away from a solid block.
There are several prominent types of 3D printing technologies, each with its unique mechanisms and applications. Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is one of the most widely used methods, particularly for prototyping and production. FDM operates by melting and extruding thermoplastic filaments through a heated nozzle, building the object layer by layer. Stereolithography (SLA) employs a laser to cure liquid resin into hardened plastic, allowing for high detail and accuracy, mؤaking it suitable for applications requiring fine features, such as dental or jewelry models. Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) utilizes a laser to fuse powdered materials, typically plastics or metals, into solid structures, which can be advantageous in producing complex geometries and functional parts.
Materials utilized in 3D printing are diverse, encompassing a range of plastics, metals, and even biofabricated substances. Plastics such as PLA and ABS are common in FDM, while SLA often employs various photopolymers. SLS can utilize nylon powders and metals like titanium or aluminum, providing a balance between strength and weight, which is crucial in aerospace and automotive applications. Over the years, 3D printing has evolved significantly, beginning in the 1980s with the first patents and prototypes. Its journey has reshaped industries, from healthcare with bioprinting organs to custom consumer products, showcasing how innovation in 3D printing technology can unlock creativity and efficiency in design and production.
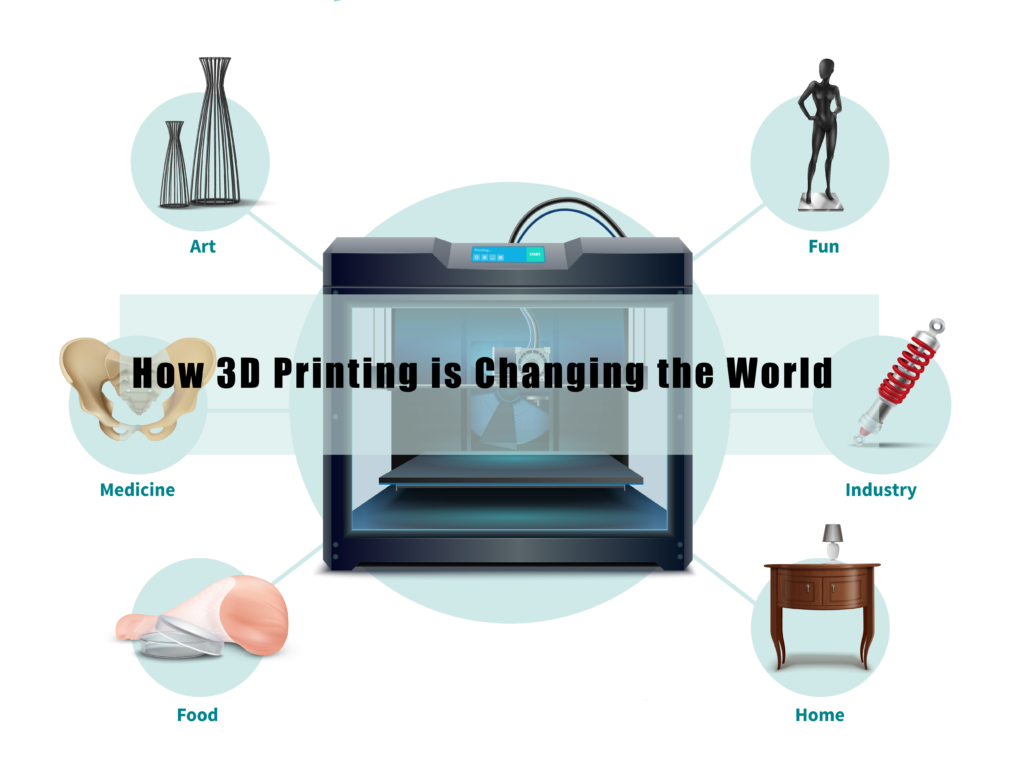
Applications of 3D Printing Across Industries
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has significantly impacted a variety of industries by enabling enhanced prototyping, custom part production, and manufacturing efficiencies. This technology allows businesses to create products with complex geometries that are often impossible to achieve through traditional manufacturing methods.
In the automotive industry, 3D printing has transformed the design and production process. Companies like BMW utilize this technology to produce lightweight components, reducing vehicle weight and enhancing fuel efficiency. For instance, BMW’s use of 3D-printed brackets has proven not only to save material costs but also to shorten production time significantly, illustrating the potential for efficiency gains.
Meanwhile, the healthcare sector has also embraced 3D printing for various applications, particularly in the production of patient-specific medical devices. Custom prosthetics and orthotics, surgical tools, and even bioprinted tissues exemplify how 3D printing is revolutionizing patient care. For example, some hospitals now create custom implants tailored to the unique anatomy of each patient, leading to better surgical outcomes and faster recovery times.
The aerospace industry is another sector leveraging 3D printing for the development of complex components. Companies such as Boeing and Airbus incorporate additive manufacturing to produce parts that are both lightweight and durable, contributing to enhanced aircraft performance. By using 3D-printed components, these companies are able to significantly reduce material waste and increase design freedom, which are critical factors in aerospace engineering.
Consumer products are yet another area benefiting from 3D printing technology. Businesses can rapidly prototype new items, allowing for quicker market entry and customization options to suit individual consumer tastes. Brands such as Nike are utilizing 3D printing in their design phases, enabling the fast iteration of shoe designs that blend performance with personal style.
Overall, the versatility of 3D printing technology across industries not only leads to reduced costs and improved efficiency but also allows for innovation and creativity in product design and manufacturing processes.

Ultimate 3D Printing
Getting Started with 3D Printing: A Beginner’s Guide
Embarking on a 3D printing journey can be both thrilling and daunting for beginners. Understanding key elements such as selecting the right 3D printer is vital for achieving successful prints. The initial step involves assessing various printer types, including Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS). Each has its advantages and suited applications; thus, it is essential to consider factors such as budget, print size, and desired material compatibility.
Once the printer is selected, another critical component is slicing software, which converts 3D models into instructions for the printer. Popular options like Cura and PrusaSlicer provide user-friendly interfaces, enabling novices to easily adjust settings for optimal results. It is advisable to familiarize oneself with the software’s capabilities, as adjusting layer heights, infill density, and print speed can significantly impact the final product quality.
Choosing the right materials is equally important in the 3D printing process. Beginners often start with PLA (Polylactic Acid) due to its ease of use and environmentally friendly nature. Other materials such as ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) or PETG offer different benefits, like toughness and temperature resistance. Understanding the characteristics of each material will aid in selecting suitable options for specific projects.
Additionally, practical tips regarding design are crucial. Utilizing platforms like Thingiverse or MyMiniFactory provides access to a wide range of 3D models. Beginners should consider design limitations, such as overhangs and bridging, to avoid complications during printing. Post-processing techniques, such as sanding or painting, can also enhance the aesthetic quality and finish of printed items.
Creating an organized workspace and being aware of common troubleshooting practices will help in overcoming challenges that may arise during the printing process. Engaging with local or online 3D printing communities can provide further support and resources, fostering connections that enhance one’s understanding and enjoyment of this innovative technology.
The Future of 3D Printing: Trends and Innovations
The landscape of 3D printing is on the brink of remarkable transformation, driven by emerging trends and groundbreaking innovations. One significant area of advancement is in materials science. Researchers and engineers continue to explore and develop new materials that enhance the functionality and durability of 3D printed objects. For instance, the introduction of biocompatible materials has opened avenues in medical applications, allowing for the creation of custom implants, prosthetics, and even organ structures with improved compatibility to human tissues. This progress underscores the pivotal role of material advancements in the future of 3D printing.
Another notable trend is the progression towards multi-material printing technology. This innovative approach enables the fabrication of complex structures from diverse materials within a single build process. This capability not only enhances design flexibility but also improves the functionality of printed objects by integrating different properties, such as rigidity, flexibility, and conductivity. Industries such as automotive and aerospace are particularly excited about these advancements, as they can manufacture lightweight yet durable components, improving overall efficiency.
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and automation is another hallmark of the evolving 3D printing landscape. AI algorithms can optimize designs and streamline production processes, significantly reducing lead times and minimizing errors. As these technologies become more refined, the capabilities of 3D printing will expand, allowing for more user-friendly interfaces and automated systems that can adapt to various printing needs.
Furthermore, 3D printing presents a promising avenue for sustainability. By allowing for on-demand production, it can drastically cut down on waste associated with traditional manufacturing methods. The potential to create items locally may also reduce transportation emissions, thus contributing to a more sustainable future. This dynamic technology could impact various sectors, from construction, where entire structures can be printed with minimal waste, to healthcare, where personalized medication could be manufactured on-site. The future of 3D printing is poised to redefine our engagement with technology, from innovative designs to sustainable practices, truly transforming our daily lives.